Fintech companies often grapple with hurdles related to accessing critical financial data and reducing customer onboarding friction, hindering their innovation and growth potential. On the other hand, banks face the twin pressures of regulatory compliance and the need to improve the customer experience and remain at the forefront of innovation.
But what if there were a bridge that could connect these two worlds and provide solutions for these challenges?
Open banking, with its innovative APIs and data-sharing ecosystem, arises as the answer. This transformative framework offers fintech companies access to the financial data they need, spurring innovation and offering cost-effective solutions. For banks, open banking ensures regulatory compliance and enriches the customer experience, fostering competition, partnerships, and new revenue streams. In this article, we’ll delve into understanding the concept of open banking and how API is used in open banking; we’ll also cover the benefits and challenges of open banking API integration and take a look at some of the examples. So, don’t miss what’s coming up next.
What is open banking API integration?
First and foremost, let’s define what is open banking API integration. Open banking API integration is the process of connecting and harmonizing various financial systems, including banks, non-bank financial institutions, and third-party service providers, through standardized Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These APIs allow the exchange of financial data and services, allowing customers to share their data with authorized third parties and access a wide range of financial products and services.
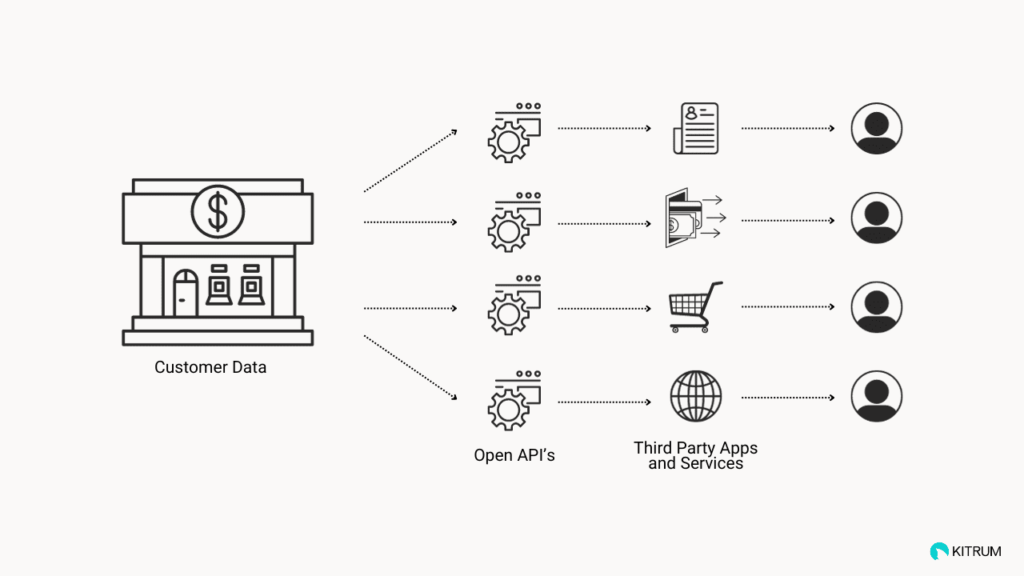
How is API used in open banking?
In the context of open banking, an API is a technology that allows communication and data exchange between a financial institution (such as a bank) and a third-party service provider (which could be a fintech company or any other external entity). The API serves as a bridge, allowing the third-party service to access and retrieve specific data from the financial institution’s systems with the user’s consent, of course.
By simply checking a box in an online app’s terms of service, customers grant third-party providers access to their data. These providers can then leverage this information, including transaction history and financial relationships, for tasks such as offering diverse financial services, creating marketing profiles, or initiating transactions on behalf of the customer. Open banking aims to boost competition, innovation, and customer empowerment in the financial sector, all while prioritizing data security and regulatory compliance.
According to Statista, in 2023, the value of open banking transactions globally reached an impressive $57 billion, with expectations of significant growth in the years ahead. The number of open banking API calls, the technological backbone of secure data exchange, is projected to surge, reaching a staggering 580 billion by 2027. Notably, Europe has witnessed remarkable adoption, with third-party providers (TPPs) increasingly operating within the European Economic Area (EEA) under the passport scheme.
What are the advantages of API for open banking?
As a financial institution, you can harness the power of open banking APIs to enhance your income through one or more of the following methods:
Better user experience
By using open banking APIs, banks can provide access to a broader spectrum of financial services and applications, offering customers the flexibility to manage their finances with greater convenience and efficiency. This enables them to access third-party tools for budgeting, investment, payments, and more, all within a unified and user-friendly interface. Such integration allows customers to view their financial landscape; it also provides tailored financial solutions, and thus, customers have greater trust and satisfaction.
Increased income
Banks can diversify their income streams by providing Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS). By offering third parties access to their database via APIs for a fee, banks create a new source of revenue. Besides, open banking and data collection give you a better understanding of how customers behave and what they like. With this knowledge, you can make your products more appealing and create personalized marketing campaigns that lead to increased revenue.
Valuable partnership
Banks can leverage API integration to collaborate with innovative fintech companies, expanding their service offerings without requiring extensive in-house development. This allows them to tap into fintech’s agility and customer-centric solutions, creating a win-win scenario that attracts new customers and bolsters revenue. Conversely, fintechs can access established banking infrastructure and customer data, accelerating market entry and improving service quality.
Payment as a service
Open banking APIs offer the advantage of building faster and more secure payment infrastructure, helping users to make payments without entering card details. APIs improve payment transparency and scalability by allowing individual transactions and bi-directional processing. Open banking APIs improve existing payment methods like ACH and wire transfers and the adoption of modern payment methods like Real-Time Payments (RTPs) and Pay-By-Bank. Moreover, they facilitate Payment Initiation Service (PIS), where a licensed third party can initiate payments on behalf of customers without sharing sensitive information, ensuring quick and secure money transfers to the merchant’s account.
Open banking API integration challenges
Everything seems too good to be true; what are the disadvantages of open banking, you might ask then? Surely, while open banking offers numerous advantages, it’s not without drawbacks. As the financial landscape undergoes a transformation marked by increased data sharing, things like privacy concerns and security risks come to the forefront. Let’s take a look at the main drawbacks:
Privacy and data security
With the fact that open banking API involves the sharing of sensitive financial information, many people might ask, “Is open banking API safe?” Well, it is true that by sharing sensitive financial information between banks, third-party providers, and customers, there is a heightened risk of data breaches and privacy violations. As consumers trust their financial data to these systems, robust security measures, encryption protocols, and authentication methods must be in place to safeguard this information.
Regulatory compliance
Financial institutions and third-party service providers must navigate a complex web of regulatory requirements and standards, often varying by region. For example, in Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) places stringent demands on data privacy and consent, while the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) governs payment services and data sharing. Compliance with these regulations and others is essential to ensure that customer data is handled in a legally sound and ethical manner.
Establishing customer’s trust
Open banking entails customers sharing their data and using services from various providers, which can raise concerns regarding service quality, reliability, and value. Customers may lack awareness or clarity about the benefits and risks of open banking, as well as how to use the APIs effectively. To address these challenges, providers must educate customers on the advantages and drawbacks of open banking, clarify their rights and responsibilities, and emphasize the convenience and value of their services.
Technical complexity
Open banking API integration is challenging because it involves connecting and organizing data and services from different financial institutions that use varying systems, data formats, and standards. This requires complex mechanisms for transforming and mapping data to make everything work together smoothly. Financial institutions might also employ distinct data standards and protocols, requiring third-party providers to adapt and understand these varying standards, leading to compatibility issues and increased development and testing time. Besides, variances in API authentication methods, data endpoints, and usage limitations introduce further challenges.
Infrastructure & engineering costs
Infrastructure costs in open banking integration can be a substantial financial burden, especially for smaller financial institutions. Establishing the requisite technological infrastructure to support secure data sharing, API management, and data storage demands a significant upfront investment. Investment usually includes the development of robust API gateways, security protocols, and data centers capable of handling large volumes of sensitive financial data.
Operational expenses include server maintenance, cybersecurity measures, and system upgrades to ensure data security and regulation compliance. For smaller institutions, it can be challenging to allocate the necessary resources, both in terms of capital and technical expertise, to build and sustain this infrastructure.
What is an example of open banking API?
As we have explored the advantages and challenges of open banking integration API, it is time to delve into some real-world examples that highlight the potential of open banking. Here are some of the open banking API examples:
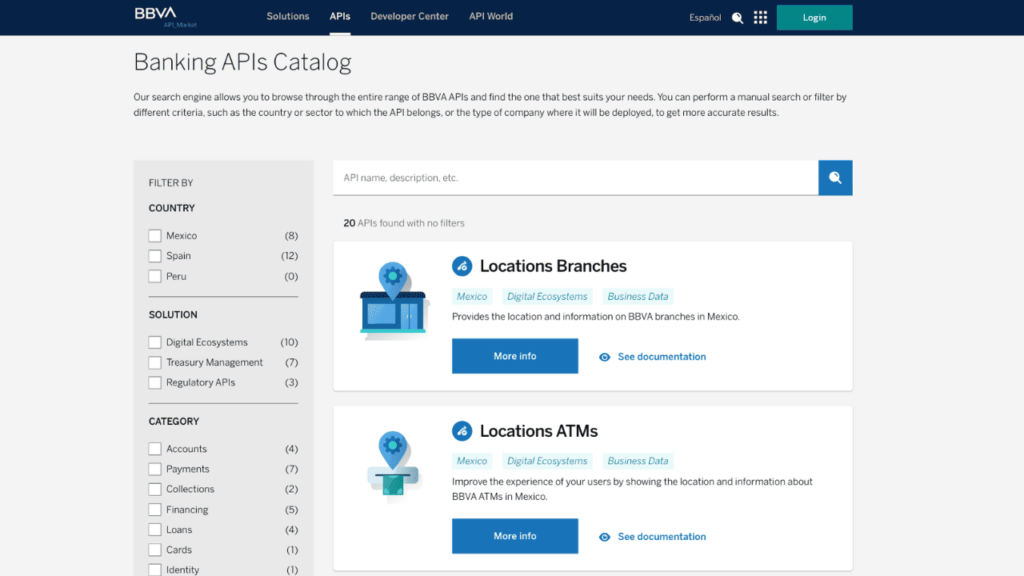
BBVA API Market
BBVA has introduced a comprehensive open banking initiative named BBVA API Market, offering a broad array of APIs that cover account details, payment initiation, transaction history, and more. These APIs allow developers to access real-time account information, facilitate payments, and effectively manage finances. In addition to the versatile API selection, the BBVA API Market extends its support to developers with an array of resources, including documentation, code examples, and a dedicated support team.
HSBC
HSBC offers a wide range of APIs catering to diverse corporate banking needs, making global transactions and financial management more seamless. From account information, balance, and transaction reporting to treasury, payments, and trade finance solutions, these APIs give the power to businesses to optimize their financial operations. Besides, HSBC’s treasury APIs encompass credit notifications, direct debit collections, global disbursements, payment initiation, payment pre-validation, SWIFT gpi for cross-border payments, and sandbox management API for easy data management.
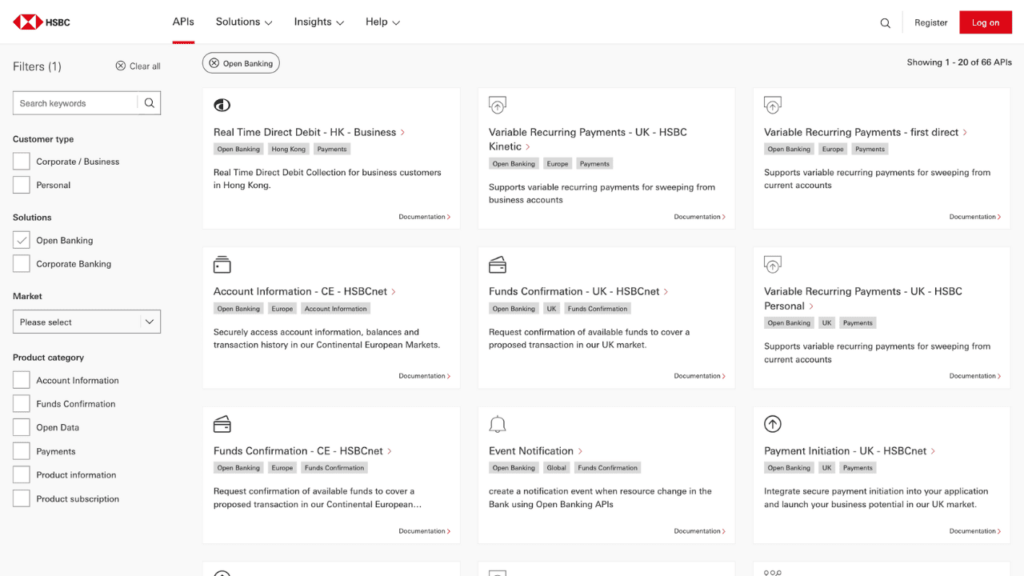
On the trade finance front, HSBC provides APIs for bank guarantees, seller loans, import and export collections, letters of credit, point of sale finance, buyer loans, trade working capital, receivables finance, and supply chain finance. Moreover, the omni-collect API streamlines payment methods for improved corporate payment processing. These APIs are supported by comprehensive documentation to facilitate integration and use the full potential of these banking solutions.






