What is the connection between music and engineering? Do music and technology seem like an unexpected duo? Not anymore. Today, tech crafts the tunes we love. In our digital era, the fusion of music and tech is a powerful collaboration where the market is rapidly growing. According to the latest research, the music production software market, which was valued at USD 447.62 million in 2022, is projected to reach USD 724.79 million by 2028, reflecting a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.36%.
In this article, we are going to discuss what is AI music software, how music software is usually created, how much it costs to build a music app, and what are some of the top features of AI in the music industry. Stay tuned and keep reading.
What is AI music software?
With AI making waves in all industries, you might be wondering: can AI be used for music production? The simple answer is yes. Moreover, about 22% of music producers use AI to improve the quality of their songs.
AI music software is applications and tools that use artificial intelligence technologies to create, compose, analyze, or improve music. These applications leverage machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and other AI techniques to perform tasks traditionally associated with human musicians and composers. AI music software can be used in various stages of the music creation process, from composition and production to analysis and recommendation.
For example, take a look at AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist). AIVA is an AI music composition software that creates classical music compositions. It uses deep learning algorithms to analyze classical music datasets and generate original compositions in various styles.
Or, take a look at Landr, an AI-driven music production platform developed by Montreal-based AI company MixGenius that offers automated mastering services. With curated samples and exclusive plugins, it effortlessly integrates into your DAW, allowing you to shape and bring your musical vision to life.
How is music software created?
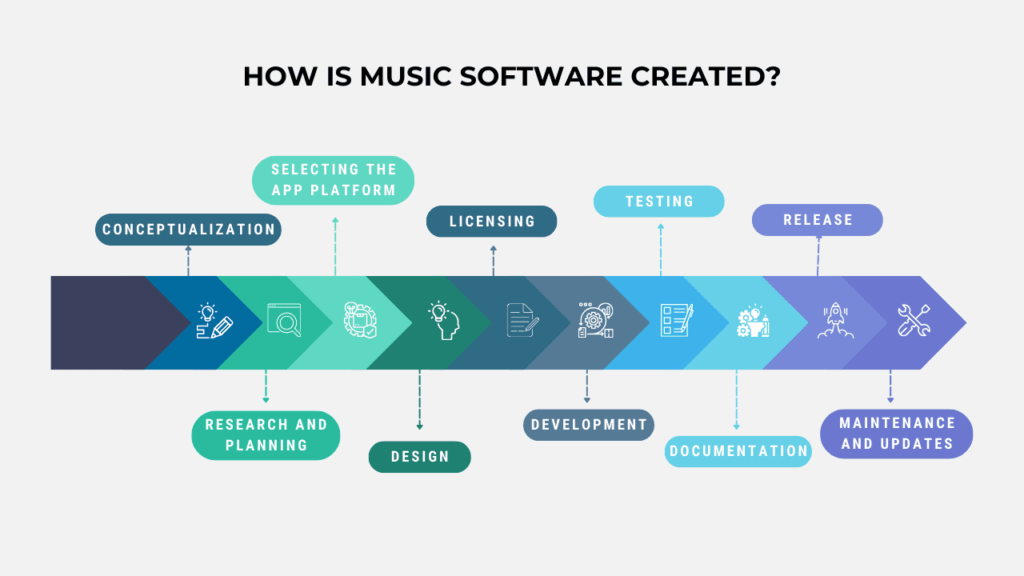
Similar to the development of any other product, crafting music software involves several key stages. Here is a simplified overview of how music software is typically created:
- Conceptualization: This stage includes the identification of the purpose and scope of the music software. Determination of the specific features and functionalities it should offer, whether it’s for composition, production, recording, or other purposes.
- Research and planning: At this stage, you typically conduct market research to understand user needs and existing solutions. Then, you plan the software architecture, defining how different components will interact. Then comes an outline of the technology stack, programming languages, and frameworks to be used.
- Selecting the app platform: Choosing the right platform for your app will influence the final cost of the development. You also need to consider factors such as the target audience, app functionality, and market trends. Carefully analyze the advantages and limitations of platforms like iOS, Android, or cross-platform solutions.
- Design: Afterwards, the UI/UX designer creates a user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design that is intuitive and user-friendly. He also designs the database structure if the software involves data storage and plans the algorithms and logic for music-related functions.
- Licensing: If your app will have someone’s compositions, then you have to think about acquiring the rights to share someone’s compositions. Copyrights and legal procedures must be adhered to, or legal consequences may follow. Obtaining a Public Performance Rights license is essential to delivering top-notch audio or video content. In the United States, this process is overseen by 3 agencies: ASCAP.com, BMI.com, and SESAC.com. Besides, a portion of the generated revenue must be allocated as royalties to compensate artists for using their music.
Remember that streaming music without permission is illegal. According to Medium, it can lead to fines ranging from a minimum of $30,000 to $150,000 per song played. Therefore, it is crucial not to overlook licensing to avoid legal consequences.
- Development: This stage usually involves writing the code according to the design and specifications, and implementation of features like audio processing, MIDI integration, or any other functionalities required for the software. There also should be a test of individual components and the software as a whole during development.
- Testing: It is necessary to conduct rigorous testing to identify and fix bugs and ensure the software works seamlessly across different devices and operating systems. The product also needs a test for performance, reliability, and user experience.
- Documentation: You also need to create comprehensive documentation for users and developers, explaining how to use the software and its technical aspects.
- Release: This stage is when you prepare the software for release. You have to be ready to address any last-minute issues and launch the software to the public or a targeted audience.
- Maintenance and updates: Finally, you monitor user feedback and address issues through regular updates. You need to stay current with technological advancements and make necessary updates to keep the software compatible and secure.
Top features of Artificial Intelligence in the music industry
AI is making a big impact in the music world. According to Sony Computer Science Laboratories, an AI music composer called FlowMachines could potentially reach 1.5 billion users. Another stunning fact is that AI is pretty good at predicting what songs will be popular, with a 77% accuracy in forecasting Top 100 Billboard Chart hits.
These facts show that AI is really changing and improving the way music is made, distributed, and enjoyed. Thus, let’s delve into some of the robust features that AI introduces to the music industry:
Improved sound design
With AI, sound design in music gets a major upgrade. It fine-tunes volume and equalization for a polished sound, throws in cool real-time effects, and smartly samples and synthesizes diverse sounds. AI adapts soundscapes based on user interaction and context, making the experience more immersive. Plus, it introduces smart virtual instruments that mimic and go beyond traditional sounds, pushing the boundaries of creative possibilities in music.
Music production assistance
Music production assistance driven by AI revolutionizes the music creation process, offering automated mixing, mastering, and sound optimization solutions. This results in improved audio quality, time efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for businesses. AI-powered virtual assistants help musicians with tasks like songwriting, chord progression suggestions, and generating melodies.
AI ensures consistent and professional standards across tracks, making high-quality production accessible to independent artists and smaller studios.
As per recent research by Ditto Music Production, 62% of independent musicians express a willingness to embrace AI in their music production processes, and 47% would use it for songwriting.
Personalized recommendation engines
Personalized recommendation engines are a game-changer. Here’s the simple magic: AI figures out what a user likes, serves more of that content, and the user is happy and stays engaged, which means they keep using the app, fostering loyalty to the platform and ultimately bringing in revenue.
Automated composition
Automated composition with AI uses algorithms to craft original music without direct human involvement. The algorithm learns from extensive music datasets, learning patterns, and styles across genres. It understands harmony, melody, and rhythm and can create entirely new compositions. This tool can help musicians overcome creative challenges and encourage experimentation, expanding the possibilities in music creation.
How much does it cost to build a music app?
The cost of building a music app is a highly individualized endeavor, influenced by a myriad of factors that collectively shape the overall expenditure.
First and foremost, ask yourself, what is the size and scope of the app? Is it music software development from scratch or improvement of already existing features?
It is also important to note that music apps come in various sizes, exemplified by giants like Spotify and more modest counterparts; thus, financial investment can range significantly. Drawing from our experience at KITRUM, the development cost for a music streaming service generally ranges from a minimum of $40,000, with the potential to increase to around $250,000 for apps that integrate advanced features and have complex UI. Yet, the ultimate pricing is contingent on your specific project requirements.
In most cases, the budgetary considerations for the upcoming app are shaped by:
Feature set
The inclusion of functionalities such as music streaming, search capabilities, playlist creation, and offline mode.
App considerations
Factors like app complexity, UI/UX design intricacy, and the targeted platform (iOS, Android, or both) are crucial in determining costs.
Team size and technology stack
A smaller team may save costs initially but could prolong the project. In contrast, a more advanced technology stack might increase expenses. Still, it significantly improves the app’s capabilities, potentially attracting a broader user base and providing long-term value for the business.
Nuanced calculation
The financial commitment for a music app is a nuanced calculation, with each project being a bespoke venture characterized by its unique combination of features, considerations, and trade-offs.
At its core, it is important to understand that the price may vary hugely, and for the best results, please schedule a consultation with a professional. Discuss your project details thoroughly, allowing the expert to understand and consider every aspect of your vision. This personalized interaction will ensure a comprehensive approach tailored to your specific needs and goals, providing a solid foundation for successful project implementation.










