At the moment, there are about 4,66 billion active internet users worldwide. The data created by users counts 1,134 trillion MB per day. All of this data is shared through social media, messengers, and different apps. As the world becomes more and more digitized and there is an app in any field of interest, users start to be more demanding of security to be sure that their data is protected. Photos go to clouds, messages are sent with various kinds of content, personal data is provided to banks, and to register in any kind of app you need to provide at least your e-mail – with every such sharing your customer must be sure that this information stays between you and him and won’t be passed further.
The breach of user’s data can cause serious damage to the reputation of your company, break the trust of your clients and result in a scandal. All of this may threaten the whole existence of your business. In 2021 there were 5,126,930,507 breached records. Ponemon Institute and IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 said the total cost of a data breach increased from $3.86 million to $4.24 million in 2021.
In July 2021 the data of 7000 million users of professional networking LinkedIn was posted on a dark web forum, revealing the information of more than 90% of its user base.
Same year Facebook faced a data breach and the information of over 500 million users appeared on another hacking forum. It included phone numbers, full names, locations, email addresses, and biographical information.
Considering all of the abovementioned, protection of customer data is both important – for you and your users. In this article, we will find out what should be considered to protect the digital data of your customers, as well as what aspects are essential to comply with The General Data Protection Regulation.
The new and old European Union cybersecurity regulations to consider
On 13 May 2022, the European Union agreed upon new regulations in cybersecurity due to the rising number of cyberattacks. You should consider those new rules if your services operate within the EU.
Data Protection According to NIS2
According to NIS2, all sectors under the directive, such as energy, transport, health, and digital infrastructure, are obliged to provide thorough cybersecurity risk management and reports. All medium-sized and large entities are enforced to follow the directive. Healthcare providers, pharmaceuticals, ICT managed service providers, courier services, manufacturers, units involved in the food chain, waste and water management, public administration entities, operators of ground-based infrastructure, supporting space-based services, digital infrastructures such as content delivery networks and data center service providers, social networks and providers of electronic communications networks or services are among them.
NIS2 requires implementing organizational security measures to manage the risks by holding senior management accountable for deploying sufficient security standards. Also, the supervisory authorities have the right to perform inspections, and security audits, request information, and demand to stop performing certain operations or inadequate risk measures.
Also, the regulation expands the incident report obligations, whereas if the incident results in a “significant impact,” such as disruption of the service, financial losses for the unit, or material or non-material losses for private or legal persons, the company should notify competent authorities within 24 hours. The follow-up and final report should be provided within a month. As well as, the general public should be notified if the case is serious.
Also, higher administrative fines will take place. In each Member State, it is required to set a precise amount or 2% of worldwide turnover for essential units. Though the final fixed amount is not settled yet, the EU proposes the sum of €4m.
If your app or website has users from the EU, you should ensure compliance with The General Data Protection Regulation. The main issue to consider is that your users should give active consent to collecting their data. You should notify them what kind of data you collect together with providing any tool to click and confirm their agreement for it. Each user should know the purpose of data collection and be able to access his data.
Data Protection According to GDPR
According to GDPR, users can request their personal data, and it should be provided within 30 days. Iff the data is too large or complex this period can be expended. Also they may request to change the information in case they find it inaccurate.
The individual can also restrict their data usage if it is inaccurate, unlawful, doesn’t meet the originally stated purpose, or a person objects to data processing. Also, they have a right to “data portability”, which ensures that they can transmit their data to another platform without interference from your business. If the user finds that the information collection is performed due to legitimate interest, performing a task or exercising official authority, or profiling, direct marketing, or processing for historical or scientific research, he can request to stop processing their data.
These are the brief description of the regulation you have to consider if you aim to provide services within the EU. Do not hesitate to learn the details more precisely before building your app or website for them to compile with the general law of the European Union.
Challenges to consider while maintaining your user’s data privacy
Most internet users confirm that they don’t control anymore of how their data is used. When we search for a specific product, from a new laptop to a book, all of the web pages are covered with commercials. This all happens due to tracking, as advertising networks and social media use pieces of code that are spread across the web.
The information of users left within the web is used to further provide customers with a better experience and show them offers and services that correspond to their interests. The only problem is that the end-user rarely permits such tracking. Browsers can get information about your IP address, user agent, location, browser plug-ins, hardware, and even your battery level.
Usually, the cookies of third parties are used within a website for tracking the activity. The tracker is notified if users come across the same cookies on a different website. In such a way, the third party creates a certain user profile.
So how can you, as a web developer, secure your customers? The first step is to provide your users with Do Not Track settings, with the help of which they may choose whether they want their information to be gathered or not. Implementing DNT, you should work on its policy applicable on your website or app and inform your users about it.
Another thing you should consider is the way to protect your user privacy by performing web analytics. This tool is vital for you as you want to understand how your audience uses your site. To protect your client’s data, your analytics provider should make your users anonymous, limit track cookies to your domain, and won’t pass the information about your users to other parties. For example, Google Analytics is obliged to anonymize users’ IP addresses, it doesn’t track them or share information with anyone else.
To maintain user privacy, but still be able to analyze their data to receive insights, working with any analytics provider you should consider an opt-out mechanism, as well as delete their logs within a couple of months, set the cookies to operate for a limited time, and respect and provide a Do Not Track tool.
If you can’t avoid user tracking, consider providing de-identification of collected information. It ensures that a person can’t be identified by the data he created. Though the tool has its vices, as any combined data sets, even de-modified, can lead to user exposure. Think of differential privacy cryptographic techniques to ensure that your users can’t be identified by any means. This tool provides information about patterns of groups within a dataset, omitting to specify each user individually.
What is HTTPS connection, and how does it work?
Giving preference to HTTPS connection over standard HTTP, you ensure that your users are not subjected to advertising flood, content changes, and unauthorized tracking. Through HTTP, a computer requests a resource through a URL, and the server responds with the source’s HTML page. The main issue is that the customer’s information, like IP address, location, and browser information, is not encrypted and can be reached by any network operating within the user’s browser and the server.
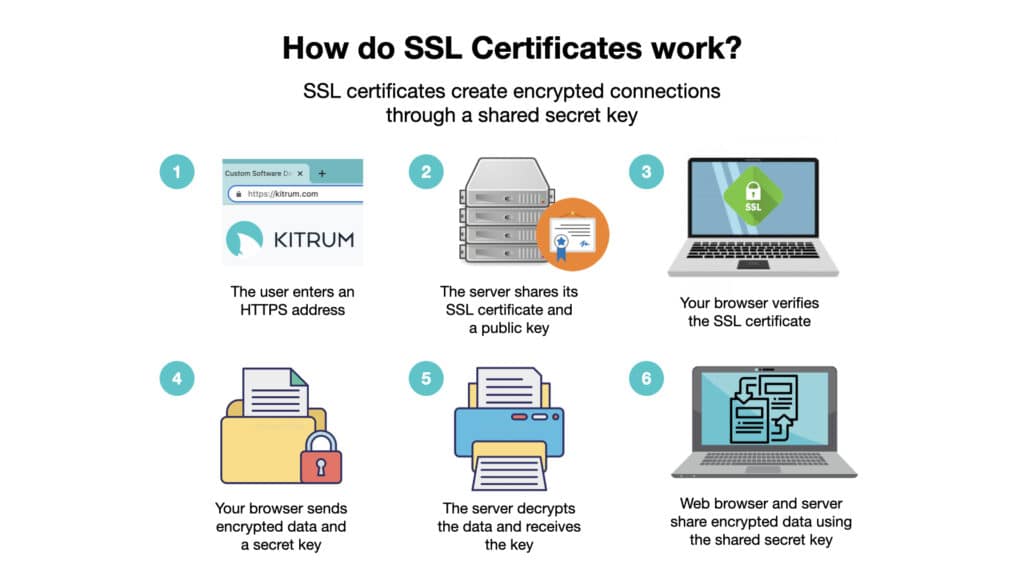
HTTPS, in return, adds additional Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) encryption, enabling encryption of requests and responses. A TLS certificate also proves the authenticity of the domain and provides a public key for exchanging it with a user’s browser.
First, the user’s client accesses the server and requests the HTTPS resource. The server requires information about the user’s connection, as supported by the TLS version. After this, it responds with a TLS certificate that verifies the domain and a public key. Then the server receives the encrypted request for the URL from the browser. A server decrypts information and sends a resource back to the client in the encrypted form. In the end, it is decrypted on-premises.
Why use an HTTPS connection?
As long as many users may be unaware of such tools as Do Not Track browsers settings, HTTPS is one of the most reliable tools to maintain the security of your user’s data. The value of an HTTPS connection lies in the protection of the data privacy of the user and its security, as well as the approved authenticity of the domain.
It gives the user an encrypted connection to your site while his information remains private. HTTPS doesn’t let third-parties monitor sites and doesn’t reveal customers’ web traffic to the attackers. By providing the authenticity of the domain and its content so that users can trust your site and the content it produces.



