Big Data and IoT are booming technologies that are becoming increasingly popular. You see them everywhere, from smart home devices like thermostats and security cameras to wearable fitness trackers and industrial sensors on manufacturing equipment.
These devices make life easier, from creating grocery lists to adjusting the brightness of lamps. They’re also changing how cities are developed, making them smarter and more efficient.
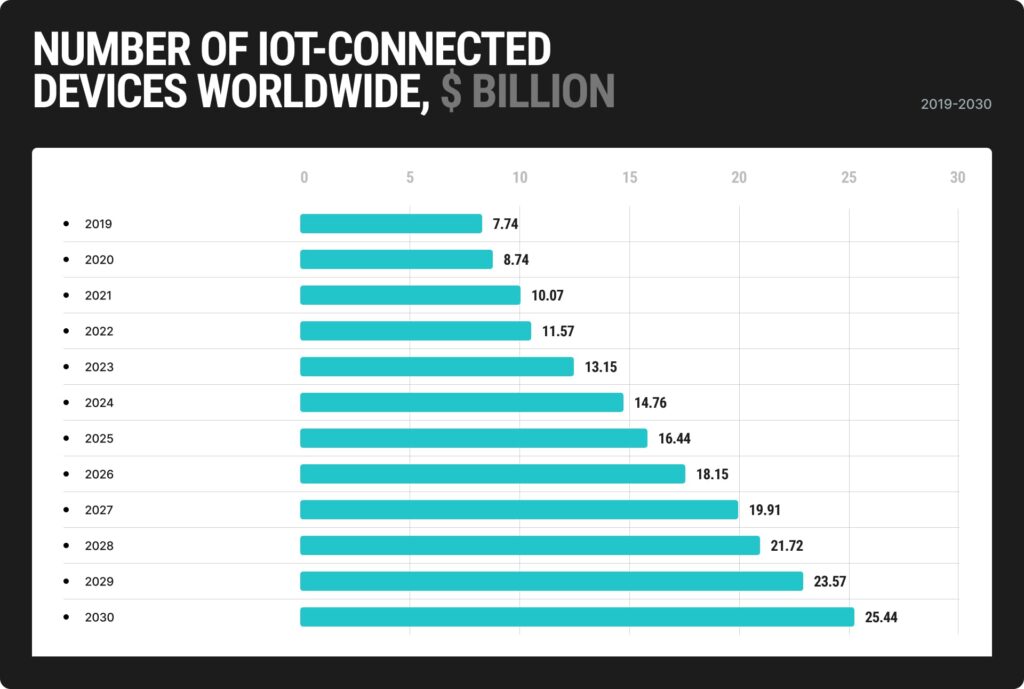
According to most recent calculations, there are over 14 billion connected IoT devices worldwide. Moreover, it’s expected that there will be approximately 25.44 billion IoT devices by 2030.
IoT also revolutionizes various industries, including healthcare and FinTech. In the healthcare industry, IoT enables personalized patient care through real-time monitoring and early intervention. In FinTech, IoT enhances security and efficiency in financial transactions while providing valuable insights for product development and risk management.
So, how can leveraging Big Data improve and empower IoT initiatives for business success? More on that is in our article below.
How is Big Data used in various industries?
Nowadays, world business leaders see Big Data as the next big thing. They actively research how to hire Big Data developer teams, as owning it means that all of your business decisions and choices are based on the insights powered by the processed information.
Big Data development service helps companies gather potent insights to create better services or products and reach target audiences through more accurate marketing campaigns. Organizations operating in the medical field can use big data in healthcare to make discoveries, such as risk factors of various diseases, and help with diagnostics. Lots of this data can be received through IoT medical devices through constant monitoring of patient health metrics or groups with specific health issues to make further analyses. It can be done with remote patient monitoring.
In FinTech, Big Data is employed through advanced analytics techniques such as ML and AI to process large volumes of financial data from various sources like transactions, market trends, and customer behavior. This analysis allows FinTech companies to derive valuable insights, identify patterns, predict future trends, assess risks, and tailor financial products and services to meet specific customer needs more accurately and efficiently. Besides, big data analytics helps detect fraudulent activities by identifying unusual patterns or anomalies in transactions, improving security measures, and safeguarding financial systems.
How do IoT and Big Data relate to each other?
The relationship between IoT and Big Data is symbiotic, as IoT devices generate vast amounts of data that can be harnessed and analyzed using Big Data technologies. Based on the most recent calculations, approximately 328.77 million terabytes of data are produced daily. Statista estimates that by 2025, the cumulative data volume from connected IoT devices worldwide is expected to reach 79.4 zettabytes (ZBs). It is a significant data set within the Internet, making IoT the largest supplier of Big Data.
So, how Big Data can be used in IoT? IoT devices collect and transmit data from various sensors and sources, ranging from temperature sensors in smart thermostats to vehicle GPS trackers. Often unstructured and in real-time, this data holds valuable insights that can drive informed decision-making and optimize processes across industries.
Big Data analytics enables organizations to aggregate, process, and analyze this massive influx of IoT-generated data, uncovering patterns, trends, and correlations that were previously inaccessible. Businesses can derive actionable insights from IoT data streams by leveraging advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning and predictive analytics. The result? Improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and the development of innovative products and services.
How Big Data is used in IoT?
Big data in IoT serves as the backbone for extracting actionable insights from the massive amounts of data generated by interconnected devices. Let’s break down how exactly big data is used in IoT.
Data aggregation
Big data technologies collect, aggregate, and store vast data generated by IoT devices, including sensor readings, machine statuses, environmental conditions, and user interactions.
Data processing and analysis
Advanced analytics techniques like ML, statistical modeling, and anomaly detection are applied to IoT data streams to extract valuable insights. This involves processing data in real-time or near real-time to identify patterns, trends, correlations, and anomalies.
Let’s look at remote patient monitoring systems in the healthcare industry. Wearable IoT devices, such as fitness trackers and medical sensors, continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and health metrics remotely. Through big data analytics, these systems provide insights into patient health trends, detect anomalies, and predict potential health issues.
Predictive maintenance
By analyzing historical and real-time IoT data, predictive maintenance models are built to anticipate equipment failures or maintenance needs. This helps schedule maintenance activities proactively, reduce downtime, and optimize asset performance.
For instance, General Electric uses IoT sensors and big data analytics to predict maintenance needs for its jet engines. Predictive Maintenance involves detecting and predicting failures in machine components to prevent downtime and optimize maintenance planning. These technologies offer real-time monitoring, proactive diagnostics, and usage-based maintenance recommendations, ultimately reducing costs and maximizing fleet operations.
Optimization of operations
Big data analytics in IoT enables optimization of operational processes by identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas for improvement. This can include streamlining supply chains, optimizing energy usage, or improving production workflows.
Look at smart grids for energy management. IoT devices installed across power grids gather data on energy consumption, weather conditions, and grid performance. Big data analytics processes this information to optimize energy distribution, predict demand spikes, and prevent outages. For example, Siemens uses IoT and big data to optimize energy distribution, predict demand spikes, and prevent outages in smart grids, ultimately enhancing energy efficiency and reliability.
Personalization and customization
By analyzing IoT data related to user behavior, preferences, and interactions, personalized experiences, and customized services can be delivered to customers. For example, in smart home systems, lighting, temperature, and entertainment preferences can be automatically adjusted based on user habits.
Improved decision-making
Insights derived from big data analytics in IoT empower decision-makers to make informed and data-driven decisions. This can range from optimizing retail inventory levels based on demand forecasts to adjusting traffic flow in smart cities based on real-time congestion data.
For instance, Transport for London (TfL) uses big data and IoT to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of its public transport network. TfL gains insights into customer journeys and service performance by analyzing ticketing systems, vehicle sensors, social media, surveys, and focus groups. This data-driven approach allows TfL to adapt services based on customer needs, promptly track and respond to issues or emergencies, and provide tailored travel updates to improve customer experience.
Security and risk management
Big data analytics helps in detecting and mitigating security threats and risks associated with IoT deployments. This includes identifying abnormal patterns of behavior that could indicate cyber attacks or breaches in connected systems.
For instance, Darktrace uses big data analytics to monitor Industrial IoT devices for potential cybersecurity threats. By analyzing network traffic data in real-time, Darktrace’s AI can detect anomalies, unusual patterns, and potential cyber attacks, improving industrial security.

Scalability and flexibility
Big data platforms provide scalability and flexibility to handle the growing volume, velocity, and variety of IoT data. This ensures that IoT applications can effectively manage and analyze data as the IoT ecosystem expands.
Types of analytics you can use in your IoT
Big Data can provide 4 types of analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
- Descriptive analytics manages the information about the connected devices’ performance in real time. It will help you understand how your consumers use the device, spot the setbacks or errors, or identify its location.
- Diagnostic analytics explains why particular actions happen within your device, such as why it works in a specific way and what causes different outputs.
- The most valuable insights from big data in IoT can be received through predictive analytics, as it can provide you with assumptions on how your device can function in the future by analyzing past data with the help of machine learning. It can help you foresee what processes are challenging for your device so that you can use this information for an upgrade. You can use it for service, anticipation failures, or specific needs before your machine breaks down.
- Perspective analytics gives you an understanding of how to affect the predicted information.
Future of IoT and Big Data in the business
Considering that the number of IoT devices is growing rapidly, we are entering an era of unprecedented connectivity and data generation. With the global market projected to soar to $50.9 billion by 2026, IoT and big data will continue to revolutionize business operations across various sectors.
For example, supply chains will be optimized through IoT devices tracking inventory levels and shipment conditions, while big data analytics provide insights to improve efficiency. Customer personalization will reach new heights as IoT-connected devices gather data on behavior and preferences, allowing businesses to deliver personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
Smart retail solutions will use IoT sensors to monitor store traffic and analyze customer behavior, leading to optimized store layouts and improved shopping experiences. Energy management will become more proactive with IoT-enabled building systems, reducing costs and promoting sustainability. Health monitoring and telemedicine will advance through IoT-enabled medical devices, providing remote patient monitoring and personalized treatment plans.
Finally, smart agriculture will leverage IoT sensors to monitor crop conditions and optimize farming practices, maximizing yields and sustainability.
Notably, Big Data in IoT as a service is expected to surge to $7.3 billion by 2026, with North America emerging as a frontrunner in this burgeoning market. As organizations continue to harness the power of Big Data analytics to derive actionable insights from IoT-generated data, they will gain a competitive edge, drive innovation, and unlock new opportunities for growth and success in the dynamic landscape of business.






