LLMs and Generative AI in Healthcare: Its Capabilities and Limitations
According to research from Stanford, 62% of a doctor’s time is spent with the electronic medical record and not with the patient. Can you feel the burden of administrative tasks in healthcare? This is only one issue out of hundreds that generative AI can help solve.
In a survey conducted in December 2023, numerous healthcare provider organizations indicated active implementation of LLMs and generative AI technologies. Gartner’s survey results indicate that between June and December 2023, there was an increase in the evaluation of use cases, policy development, and funding. The current top priorities involve using large LLMs and generative AI to alleviate clinician and administrative burnout.
Thus, we can see that LLMs and generative AI hold significance for both medical institutions and patients. In today’s article, we are going to break down topics such as how Gen AI is used in healthcare and its capabilities and limitations. Let’s begin!
What is generative AI, and how is it going to impact healthcare?
Before we delve into the capabilities and limitations of generative AI in healthcare, let’s understand the whole concept of generative AI and which role it plays in the healthcare industry.
Generative AI refers to AI technology capable of generating new content based on input data, such as images, text, or even entire scenarios. In healthcare, generative AI holds immense potential to revolutionize various aspects of patient care, medical research, and education.
Imagine generative AI as a highly advanced artist that can create lifelike paintings from scratch, using only a few initial brushstrokes as guidance. Similarly, in healthcare, generative AI can analyze vast amounts of medical data and produce novel insights, diagnoses, or treatment recommendations.
For example, consider a scenario where a radiologist inputs a set of medical images into a generative AI system. Instead of merely assisting with image analysis, the AI could generate predictive models for disease progression, helping clinicians anticipate future outcomes and plan interventions accordingly. This ability to predict and forecast medical conditions could significantly improve patient care by fostering proactive and personalized treatment approaches.
Capabilities of LLMs and Generative AI in healthcare
Below, we will discuss how LLMs and generative AI can revolutionize the healthcare industry, from streamlining workflow and accelerating processes to enhancing patient care, education, and training. So, how AI can be used in healthcare?
Gen AI gives efficiency and time savings
Medical staff is often occupied with patient consultations, diagnostic procedures, treatment planning, and administrative tasks. AI-driven solutions can help healthcare providers to work more efficiently and automate routine tasks. For example:
Streamlined workflow
AI can streamline clinical workflow by integrating with healthcare IT infrastructure. This includes interoperability solutions, smart electronic health record (EHR) interfaces, and workflow automation tools. In this case, AI effectively reduces the need for manual data entry, improving overall productivity within healthcare settings. Through automation and intelligent processing, AI systems optimize the flow of information, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
For instance, there is a tool called DeepScribe that operates by using a microphone, similar to an Amazon Echo, during medical visits. It employs voice recognition and natural language processing to differentiate between the doctor’s and patient’s voices. Through generative AI, DeepScribe can create medical notes in the format typically used by physicians, including sections like chief complaint, history of present illness, past medical history, family history, and social history.
This eliminates the need for physicians to manually transcribe notes, saving them valuable time during patient consultations. DeepScribe is already implemented by Stanford Health Care, Texas Medical Center, Berkeley University of California, and others.
Saving time
Healthcare providers spend a lot of time and resources manually preparing prior authorization requests for insurance companies for medical procedures. What if Gen AI would do this instead?
For instance, Doximity GPT offers a solution that automates the generation of prior authorization letters. Healthcare providers can input patient and procedure information into the platform, and Doximity quickly generates detailed letters tailored to the specific procedure and patient, including clinical justifications and references. This streamlines the prior authorization process, saving healthcare providers valuable time and resources and ensuring timely patient access to necessary medical procedures.
Reducing errors
This streamlined approach not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of errors associated with manual data entry, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. However, it’s important to always double-check the documentation that AI wrote.
Navigating document complexity
Physicians often struggle to navigate and comprehend extensive medical policies and insurance documentation efficiently. With documents spanning hundreds of pages and filled with intricate details, finding specific information quickly becomes daunting, leading to delays in patient care, potential errors, and increased administrative burden on healthcare providers.
Unriddle AI addresses navigating and comprehending complex healthcare documents, such as insurance policies and medical guidelines. Unriddle AI streamlines searching and understanding these documents, allowing users to input queries or ask questions and receive clear, concise answers or summaries. This solution eliminates the need for manual searching through pages of text and improves accessibility to crucial healthcare information, ultimately saving time and enhancing comprehension for users.
Optimized resource allocation
AI optimizes resource allocation in healthcare by analyzing data to forecast patient demand and allocate staff efficiently. Automated scheduling systems create fair schedules, saving time and minimizing errors. This prevents understaffing, reduces overwork, and improves work-life balance for medical staff.
On the other hand, optimization of resource allocation can look like next. Imagine a patient arriving at a doctor’s office with overwhelming background documentation. Manually reading and analyzing this extensive medical record would be time-consuming for the doctor. However, by leveraging AI technology, the doctor could quickly and accurately summarize the patient’s current state or extract specific details, which he would need hours and hours to look for without the help of AI.
Fraud prevention
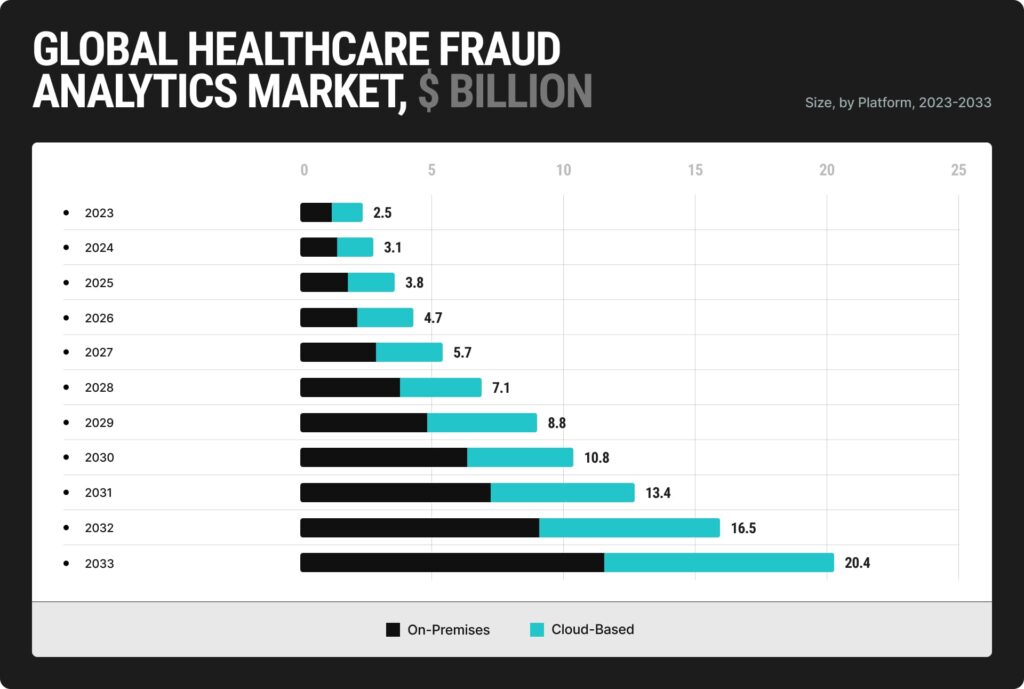
Fraud prevention has become a paramount concern in the healthcare industry, with the Global Healthcare Fraud Analytics Market poised for significant growth in the coming years. According to a recent report, the market is projected to soar to approximately USD 20.4 Billion by 2032, marking a substantial increase from USD 2.5 Billion in 2022. This remarkable expansion is attributed to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.5, expected between 2023 and 2032. As healthcare fraud continues to pose severe financial and reputational risks, adopting advanced analytics solutions is essential for detecting and preventing fraudulent activities and safeguarding the integrity of healthcare systems worldwide.
Gen AI delivers a patient-centric approach
AI technologies can be used to prioritize patients’ needs and experiences by personalizing treatment plans, improving communication between patients and healthcare providers, or enhancing the overall healthcare experience. Let’s see how it’s possible:
Virtual medical assistance
We have all complained about long queues at the doctor’s office at least once. Thus, many people have started to use virtual medical assistance. According to a Rock Health report published in February 2023, 80% of respondents reported accessing care online at least once, marking an increase of 8% points from 2021.
AI virtual nurse assistants, which include AI-driven chatbots, applications, or similar interfaces, provide patients convenient access to healthcare support remotely, offering timely help with medication management, symptom monitoring, forwarding reports to healthcare providers or surgeons, and facilitating patient appointments with physicians. And all from the comfort of patients’ homes.
For example, TGH Urgent Care’s case shows that they significantly reduced daily call volumes by 40%, deflecting 40% of calls to SMS messaging by implementing LivePerson’s Voice bot AI. This integration alleviated stress on customer service teams and front desk staff, resulting in a smoother workflow, improved response rates, and a more efficient patient experience while managing an unprecedented surge in patient calls.
Better communication
According to recent studies, 83% of patients said poor communication was the worst part of their experience. Fear not, as AI technology can solve this problem, too. AI improves communication between hospitals and patients by providing benefits such as automated appointment reminders, personalized health information delivery, 24/7 access to support via chatbots, remote monitoring for timely interventions, medication management assistance, and post-discharge support.
Patients receive timely reminders, tailored health advice, and round-the-clock access to assistance, improving their engagement, satisfaction, and adherence to treatment plans. AI-driven solutions streamline healthcare processes, leading to better patient outcomes and experiences throughout their healthcare journey.
AI makes diagnoses more accurate
AI holds tremendous potential to enhance efficiency in healthcare diagnoses. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and vast datasets, AI systems can analyze medical images, patient data, and symptoms to aid in identifying and interpreting diseases.
For example, the University of Hawaiʻi Cancer Center employs artificial intelligence to enhance breast cancer risk assessment. Thus, AI serves as a powerful tool for classifying mammograms into low and high-risk categories, aiding in efficient breast cancer screening and diagnosis.
Besides, according to findings from the NCBI study, AI-powered algorithms accurately identified 68% of COVID-19-positive cases within a dataset comprising 25 patients initially diagnosed as negative by healthcare professionals.
Gen AI in education and training
Generative AI truly takes medical education and training to the next level by offering dynamic and personalized learning experiences tailored to individual needs. It enhances educational effectiveness through adaptive and interactive content delivery. Let’s see how exactly AI leverages education:
- Real-world role-playing scenarios: Imagine a generative AI-powered platform that creates virtual patient scenarios for medical students to practice diagnosing and treating various conditions, providing realistic learning experiences without the need for physical patient interaction. It’s like a bridge between theory and practice.
- Customized learning paths: What does it mean? The technology guides students through the intricacies of medical education at their preferred speed, pinpointing knowledge gaps, proposing areas for improvement, and delivering customized feedback, thereby enhancing the engagement and efficacy of the learning process.
- Creation of educational content: AI can analyze vast amounts of medical literature and research to generate up-to-date educational materials and textbooks, ensuring that medical students and professionals have access to the latest knowledge and best practices in healthcare.
- Generating case studies: Generative AI can produce case studies resembling real-life scenarios, enabling students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. These case studies can vary in complexity to accommodate learners’ skill levels. Additionally, it extends to interactive learning modules covering a broad spectrum of topics, ranging from basic anatomy to intricate surgical procedures.
Limitations and challenges of LLMs and Gen AI in healthcare
Yet, according to research, 60% of Americans still feel uneasy about their healthcare provider depending on AI. So, what is the problem with AI in healthcare, and what are the limitations of generative AI in healthcare?
Data bias
Data bias is a critical concern in developing and deploying LLMs and Gen AI. These advanced systems heavily depend on the data they are trained on, which unfortunately can harbor biases reflecting the existing disparities prevalent in healthcare.
What does “data bias” mean? Imagine a facial recognition system used in healthcare settings to identify patients. Suppose the system is trained primarily on data from one demographic group, such as individuals of European descent. In that case, AI may struggle to identify patients from other racial or ethnic backgrounds accurately. This could lead to errors in medical records, misdiagnoses, or delays in treatment for patients whose facial features are not well-represented in the training data.
Lack of transparency
We’ve already talked about the lack of transparency as a significant concern of AI in KITRUM’s previous articles, and of course, it is not an exception in healthcare. Without clear insight into how these AI models generate their outputs, clinicians may struggle to interpret and validate their recommendations, again potentially leading to errors in diagnosis or treatment.
For instance, a generative AI algorithm tasked with generating synthetic medical images may produce realistic-looking results. Still, without transparency into the data and processes used, clinicians may lack confidence in the accuracy of these images for diagnostic purposes.
Privacy concerns
As reported by Forbes, 80% of people express worry about using their personal data to train AI models, while 72% harbor concerns about the potential use of their personal data by a forthcoming powerful AI system.
The sensitive nature of patient health data, including medical records and diagnostic images, raises significant ethical and legal questions regarding consent and data protection. For example, if a generative AI model is trained on a dataset of patient images without adequate anonymization or patient consent, it could inadvertently expose individuals to privacy breaches and potential harm.
Future outlook
Looking ahead, the future of generative AI in the healthcare industry appears exceptionally promising. With the market value of AI in healthcare reaching approximately 11 billion U.S. dollars worldwide in 2021, forecasts project an astronomical surge, with expectations that the global healthcare AI market will soar to nearly 188 billion U.S. dollars by 2030.
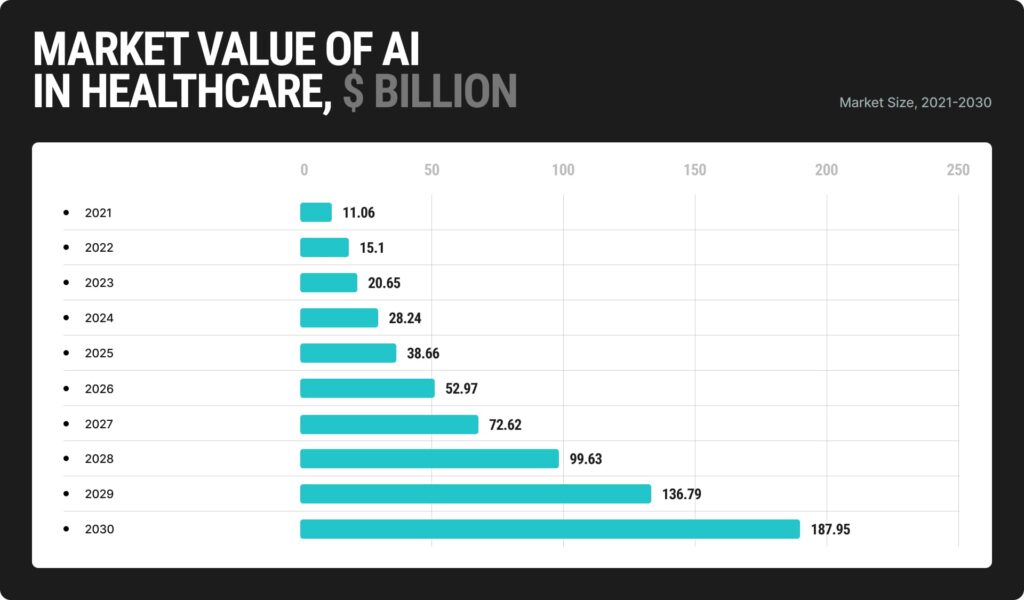
This remarkable growth trajectory is expected to surge at a compound annual growth rate of 37% from 2022 to 2030. Besides, around a fifth of healthcare organizations have already embraced AI models for their healthcare solutions, highlighting the growing adoption and recognition of AI’s potential to revolutionize patient care and operational efficiency.
Meanwhile, an overwhelming 79% of healthcare professionals foresee robotics and AI as pivotal players in significantly improving the healthcare industry, indicating widespread optimism and anticipation for the transformative impact of AI in shaping the future of healthcare delivery and outcomes.