Did you know that 90% of online consumers will never return to your website if it has a bad user experience? Also, according to Kinsta, 70% of online shoppers abandon their shopping carts due to unsatisfactory user experience (UX). Meanwhile, creating a well-designed UI can result in a remarkable increase in conversion rates of up to 200%, and when coupled with a positive UX, that figure can escalate to an impressive 400%. Without a proper UI/UX design, users would find interacting with and appreciating a product really difficult. But what exactly is the role of a UI/UX designer in the product development process? How do they shape the way users interact with digital products, and why is UI UX design important for your project?
What is the role of a designer in product development?
Developing a great UX design is similar to building a house. It is about creating functions that make the operation of a product seamless for end-users.
UI/UX designers include human-centered structures as part of the design framework by considering end-users needs and the constraints they experience when using the product. UI/UX design:
- Improve user satisfaction by creating intuitive interfaces, seamless interactions, and delightful experiences. UI/UX designers increase user engagement and enjoyment, fostering positive perceptions of the product or service.
- Improve usability. UI/UX designers focus on optimizing usability, ensuring that users can quickly and efficiently accomplish their tasks. Clear navigation, intuitive workflows, and user-friendly interfaces reduce user frustration, minimize errors, and increase productivity.
- Increase user retention. For instance, if the loading time for images is slow, 25% of customers will quit their interaction with a website. A compelling UI/UX design encourages users to stay longer on a website or within an application, reducing bounce rates and increasing user retention.
Higher conversion rates. For instance, AliExpress experienced a 10.5% boost in orders and a 27% improvement in conversion rates for new customers when they reduced the load time of their pages by 36%.
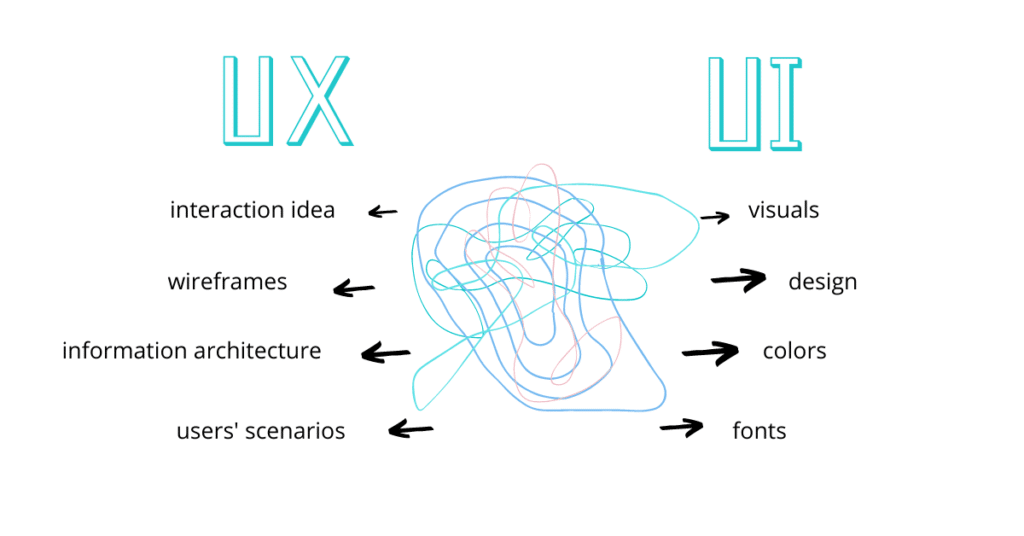
UI/UX: What is the Big Difference?
UI/UX designers mainly develop a product’s interface and practicality. Here are the disparities between both.
UI refers to the user interface of a product. This part of the design process focuses more on the visuals of the software. UI designers build the product’s software in ways that are appealing to users and easy to comprehend.
UI designers
- develop a concept for different product pages in line with the brand;
- curate content for each page;
- create responsive designs for different platforms.
UX refers to the user experience associated with said product. It encompasses different aspects of product development bordering on functionality and navigation. In essence, what they do is:
- They experiment and pick tools that suit the product;
- They improve user experience by making the product simple to use;
- They collate real-time data on customer interaction with the product and implement changes that reflect the user’s needs.
A single UI/UX designer builds the product’s UI/UX designs. The designer is a specialist responsible for creating and improving customer relationships with the product. UI/UX designers simplify the product functionalities, making it easy for users to achieve their goals with the least effort.
For the most part, UI/UX designers follow a simple guide when creating a product. They ensure product quality and customer satisfaction are met at all times. They do this by:
- Conducting proper and thorough research on the product;
- Analyzing data obtained from earlier research;
- Collating and interpreting said data;
- Developing a wireframe that reflects the core product elements;
- Building a functional prototype;
- Evaluating and iterating on all steps mentioned before.
UX designers
- are motivated to think in unconventional ways;
- experiment with non-standard solutions to achieve innovative results and,
- some parts of their functions overlap with that of other departments. Because of this, they collaborate with different sections of the company, like the business analysis department.
UI/UX designers accompany the users throughout their journey in the product interaction process.
Why is UI UX design important for your project?
UI/UX design plays a pivotal role in the success of any digital product or service. A well-crafted user interface (UI) improves a product’s visual appeal, captures users’ attention, and establishes a strong brand identity. Meanwhile, user experience (UX) design focuses on ensuring that the product is intuitive, user-friendly, and capable of fulfilling users’ needs effectively. A seamless UI/UX design not only attracts and engages users but also drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and, ultimately, business growth.
Having a UI/UX designer aboard, business owners can provide their clients with a delightful experience, differentiate themselves from competitors, and increase the likelihood of achieving their desired goals. Ignoring the importance of UI/UX design can lead to frustrating user experiences, high bounce rates, and missed growth opportunities. Hence, hiring a skilled UI/UX designer is a strategic decision that can significantly impact the success and competitiveness of a client’s digital offering.
What are the skills and responsibilities of UI/UX designers?
Building a great product that satisfies the end-users requires a lot of precision and innovation. UI/UX designers blend responsibilities like research, business analysis, and design to create a better user experience.
Research and understand the basics
Research gives UI/UX designers an insight into how the real world operates. A common mistake many designers make is building products distinct from real-life applications or being unable to solve the most pressing concerns. In a bid to be creative, they lose touch with the primary motive in developing products that do not speak to their end-users. One way to overcome this shortcoming is to carry out extensive research on the subject matter. Extensive research gives UI/UX designers an insight into how the real world operates.
Conducting research is necessary when building a new product, but there are many wrong ways of gathering information. A fallacy that has infiltrated the research space is that brainstorming is enough to give timeless insight. Brainstorming seems like an intuitive thing to do. Unfortunately, it has a lot of shortcomings that affect the quality of the answers you receive.
People have difficulties expressing their thoughts because of varied experiences and a lack of insight. You can improve the quality of findings you get by practicing ethnography. Ethnography is observing and researching people in their natural environment. Visiting real places gives you a lot of real-time data on the behavior of people and how they are likely to interact with your product. Before you begin any design, spend adequate time understanding the basics you need to build a solid product.
Define your ideal client
There are a lot of benefits to carrying out extensive research before building a product. One of such benefit is the ability to narrow down your ideal audience base. By understanding the behaviors of your ideal clients, you can create a product that speaks to them in a language they understand.
Create personas that match your ideal client by replicating their spending habits, interests, discomforts, and expectations. All this information will help you build a product with great design and a better user experience. What makes you different depends on how well you can meet your users’ needs. Anticipate their issues and provide them with a solution they didn’t know they needed.
Create an ecosystem, not just a product
The heart of the UI/UX design process is building an ecosystem. Ecosystems provide users with a well-rounded experience that leaves them more satisfied. To create a robust ecosystem around your products, consider these four things:
Complexity
Ecosystems can only thrive when all individual components are functional and compactable. As products become complex, focus on versatility, usability, and connectedness.
Total user experience
Sometimes, systems can be complex and arbitrary. Bear in mind that you need to create a design for complexity and future errors. It goes a long way to fulfill the technical needs of your clients even before they happen.
Technical needs
Sometimes, systems can be complex and arbitrary. Bear in mind that you need to create a design for complexity and future errors. It goes a long way to fulfill the technical needs of your clients even before they happen.
Technology
Consistently experiment with ways you use technology to simplify the user’s experience with the product. Investigating what type of technology is likely to securely meet your product’s needs will help you build a system your users can trust.
To develop a timeless product, you must design from the user’s point of view. You can create ecosystems that truly cater to your customers’ needs by putting into perspective their lived experiences and expectations. Ask insightful questions like what inspires them? What would they like to achieve? Are they looking for something else? Would they prefer some options over others? Where do they spend the most time? What is their lifestyle? An understanding of these questions will drastically improve the quality of your product.
Design: Creating Your Wireframe
Once you are done researching and building the basic software, the next step is to focus on on-screen development. Creating a wireframe means providing a rough sketch of all the elements you need in the product. Product elements could include but are not limited to display page, data visualization, basic actions, page layout, and product navigation. What a wireframe does is that it schematically displays what the product ought to look like and the overall functionality of the product.
When UX designers create the wireframe, they can visualize the products’ fundamental structure and experiment with ways to improve it. The wireframe exposes the product’s architecture and content hierarchy. It also responds to several concerns such as elements to be displayed on pages, why they are placed in such a manner, the most functional position, and the mode of operation.
The need for creating more drawings and describing the product extensively rather than focusing solely on creating a prototype can’t be overemphasized. Sometimes, your product may require your team to build new hardware that is compatible with certain features. You need to plan and be specific about things like lighting, blink rate, product responsiveness, and other features.
Building a prototype
After the design development process, the next step is to create the product’s prototype based on the wireframes you have designed. A prototype is not the actual product. Rather, it is an interactive product sample users, and investors can interact with. Users can scroll between pages, click buttons, and perform basic functions impossible in a theoretical wireframe. Most times, a prototype is less detailed than the final product. However, it gives developers and users an insight into the basic functionalities of the app. With this, developers can gather data on what works and needs to be iterated.
User Interface Design
For a product to be considered successful, it must:
- Adhere to the brand’s identity and reflect the ideals of the company.
- Evoke the necessary emotions in the end-users and,
- Inspire the end-users to perform a specific action.
When you build products, implement elements that distinguish you from your competitors and provide innovative solutions that make you unique. Elements in the products should be visually arranged most conveniently. Pages and screens should be responsive and easy to navigate. Elements should be easy to scan, appear at the right time, operate at the right speed, and be easy to understand.
For example, in designing the UI of RubyGarage, our designers followed the atomic design methodology. By doing so, they could map out each element in detail from scratch to finish. It is easier for the designer to remain consistent with the product theme, swiftly improve interface elements, and scale them when provided with a basic design plan. After this, the designer creates a UI guide that contains all the information developers need to expedite production and remain consistent through the project phase.
Evaluate, Analysis, and Implement
As mentioned earlier, separating system testing from usability testing is unwise. For most apps, the systems work but miserably fail when the users and their environment are taken into consideration. Although the system needs to work and hardware compatibility needs to play out well, user experience is also an important factor to consider.
You’re advised to regularly and thoroughly test your product with real people in their environment. This saves a lot of time and provides real-time feedback that can expose shortcomings. You can attend to concerns like:
Will you test the actual hardware?
On what platforms would you be testing them (just your office network? Mobile platforms? WIFI systems? Cloud-based systems?)
Under what circumstances do they work best (in the quiet, outdoors, in dark rooms, with noise?)
How to find a UI/UX designer for a project?
Firstly, clearly define your project requirements and objectives, including the scope, timeline, and budget.
Next, conduct thorough research to identify experienced UI/UX designers specializing in your industry or project type. Look for designers with a strong portfolio that showcases their expertise and creativity. Consider seeking recommendations from colleagues, industry networks, or online platforms that connect clients with designers.
But, if you are seriously ready to take your product from ‘meh’ to ‘wow,’ at KITRUM, we offer a team of skilled UI/UX designers who are masters in crafting captivating experiences. Your clients will be hooked from the first click, engaged throughout their journey, and reluctant to leave. With our designs, you can wave goodbye to high bounce rates and say hello to increased user retention, heightened customer satisfaction, and conversions.
Once you have a shortlist of potential candidates, review their portfolios and assess their design skills, attention to detail, and ability to solve UX challenges. Evaluating their communication and collaboration skills is important, as a successful working relationship is essential for successful collaboration.
Conduct interviews or portfolio reviews to gauge their understanding of your project and its design process. Besides, you can kindly request references or testimonials from previous clients to gain insight into their professionalism and reliability. Ultimately, choose a UI/UX designer who possesses the technical skills and creative flair and aligns with your project’s vision and values. Partnering with KITRUM’s UI/UX designers can ensure a seamless and engaging user experience for your project.
Conclusion
A great product is a cohesive and integrated set of experiences. UI/UX designers are responsible for the overall user interface, visual design, and user experience of the product. To do a great job, designers have to anticipate what users need. Then, they build elements that are easy to understand, access, and use. The full-stack development of products involves the UI, marketing, usability, and other parts of the system needed to give end-users a well-rounded experience.
UI/UX designers are essentially the bridge between a product and its target audience. Empower the user. Designing a product greatly transcends aesthetics. It is also about creating and building products that reflect the brand’s identity and guide users on their journey.






